Cerebral Palsy
What is Cerebral Palsy?
 Cerebral palsy is a disability that affects posture and movement.
Cerebral palsy is a disability that affects posture and movement.
Cerebral palsy is usually caused by damage to the central nervous system during its developmental phase. This damage can happen before or during a baby’s birth, but also during the first 1 to 3 years of a child’s life.
Cerebral palsy affects 1 child in 500. It has a higher incidence in premature children (in particular under 31 weeks of gestational age) and in newborns weighing less than 1,500 grams.
The disorder is defined as persistent because the injury to the brain doesn’t heal, strictly speaking, but it doesn’t worsen. What progress are the consequences especially in the musculoskeletal system.
There are different types of cerebral palsy and different ways to classify it.
Anyway the main types are:
Spastic Cerebral Palsy. It is characterized by increased muscle tone
Dyskinetic Cerebral Palsy. It is a non-spastic cerebral palsy that affects the trunk muscles more than the limbs.
Ataxic Cerebral Palsy. This types affects coordination, balance and posture.
Hypotonic Cerebral Palsy. It is a non-spastic Cerebral Palsy resulting in decreased muscle tone.
Mixed Cerebral Palsy. It is both spastic and non-spastic
Cerebral Palsy Causes
Cerebral Palsy is caused by a lesion (hemorrhage or ischemia) that occurs in the brain (brain, cerebellum and brainstem) of the child at birth or before it.
The encephalic lesion can be mainly caused by:
- a total or partial decrease in oxygen flow to the child during labor or at birth
- a maternal infection not treated and transmitted to the child during or after birth (i.e. kidney infections, urinary tract infections)
- hypoglycemia and jaundice not treated after birth
Cerebral Palsy Prevention
Some of these risk factors can be avoided with an adequate care during pregnancy and at birth but, unfortunately, it is not possible to talk about real prevention.
Cerebral Palsy Symptoms
Children affected by cerebral palsy show a neuropsychomotor developmental delay, since the first months of life.
Generally the whole body is involved but the severity may vary in the different area of the musculoskeletal system.
Cerebral palsy signs can be very different and are usually noticed before the child is 2 years old.
Parents may notice that their child has a delay in reaching certain stages of development such as sitting, crawling or walking.
The symptoms of spastic cerebral palsy, the most common type, include:
- Increased muscle tone (Hypertonia)
- Abnormal movements and postures (arms may flutter, kness cross or touch each other, scissor gait,…)
- Joints don’t fully extend (due to muscle contracture)
- Muscles weakness
- Movement inhibition
Cerebral Palsy diagnosis
A complete neurological examination is important to diagnose cerebral palsy. Some of the following tests may be performed:
- clinical examination electroencephalogram
- Head magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Once diagnosed the patient will undergo multiple follow up examinations (vision, hearing, speech, …)
Cerebral Palsy Treatment
Treatment is based on the entity of the body involvement.
Unfortunately there is no cure for cerebral palsy.
The primary goal of the treatment is to make the child as self-sufficient as possible. Treatment is based on the symptoms and the need to prevent complications. Physiatrist, physiotherapist, neuropsychiatrist are the most important figures in the life and development of the child.
Surgery also plays a key role in the life of a child with cerebral palsy: on average, a child faces three surgical procedures during their lives, depending on the severity of the disease.
In cases of chronic hip dislocation, Prof. Portinaro’s team also performs hip replacement surgery using the anterior approach on patients of all ages, thanks to the innovative AMIS technique (Anterior Mini Invasive Surgery). This is a minimally invasive anterior hip replacement surgery, a safe, quick procedure (35 minutes) with a fast recovery time (patients can return home independently after just 3 days, without the need for transfusions or drains).
Cerebral Palsy life expectancy
With PICU (Pediatric Intensive Care Unit) a lot of the premature children are maintained live. As well as with new surgical and anaesthetic procedures in general patients are surviving over the age of 55/65 years according to the body involvement.
Why choose Prof. Portinaro?
Prof. Portinaro is one of the most experienced surgeons in the world for treatment of cerebral palsy.
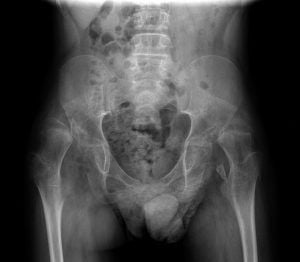 He performed more than 7,000 surgeries on children affected by cerebral palsy and he is also founder and scientific director of a non-profit organization in Italy that supports families with children affected by Cerebral Palsy and other neuromotor disabilities: Fondazione Ariel.
He performed more than 7,000 surgeries on children affected by cerebral palsy and he is also founder and scientific director of a non-profit organization in Italy that supports families with children affected by Cerebral Palsy and other neuromotor disabilities: Fondazione Ariel.
Prof. Portinaro and his team spend a large part of their work in international research projects to discover new treatments for childhood neuromotor disorders.
Main Prof. Portinaro researches and indexed publications on Cerebral palsy:
- Guided Growth of the Proximal Femur for the Management of Hip Dysplasia in Children With Cerebral Palsy.
- Can we prevent hip dislocation in children with cerebral palsy? Effects of postural management
- BT Treatment for Limb Spasticity in Childhood Cerebral Palsy
- Botulinum Toxin Treatment for Limb Spasticity in Childhood Cerebral Palsy
- Tendon structure and extracellular matrix components are affected by spasticity in cerebral palsy patients.
- The effects of femoral derotation osteotomy in cerebral palsy: a kinematic and kinetic study.
- Expression profiling of genes involved in collagen turnover in tendons from cerebral palsy patients.
- D.D.S.H.: developmental dysplasia of the spastic hip: strategies of management in cerebral palsy. A new suggestive algorithm.
- Gene expression profile of extracellular matrix of tendons in cerebral palsy.
- Bilateral hip surgery in severe cerebral palsy a preliminary review.
