Professor Portinaro at the SIMFER Congress Early Multilevel Minimally Invasive Approach
Professor Portinaro at the SIMFER Congress Early Multilevel Minimally Invasive Approach
Professor Portinaro was the only orthopedic speaker at the 49th SIMFER Congress on Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine or Physiatrics. These are very specific but also very versatile disciplines. They have biomedical roots but horizons that also extend into the social sphere.
The SIMFER 2021 congress focused on scientific aspects, on the advent of new technologies such as robotics and virtual reality, and minimally invasive and semi-invasive surgery techniques. Professor Portinaro’s speech was about this last topic.
Professor Portinaro focused mainly on the multi-level and early minimally invasive approach that has characterized his and his staff’s working method for years. This process aims to optimize the patient’s residual motor capacity.
At first, they study the patients with Gait Analysis in order to identify and quantify the problems he has, such as:
- Reduced joint movements
- Insufficient lever arms
- Altered powers
With the use of functional and minimally invasive surgery, it is possible to intervene to
- Improve joint excursion
- Correct the lever arms
- Increase powers
The other fundamental aspect of this approach is working with a multidisciplinary team. Such choice is essential because some conditions are diagnosed mainly in the physiatric field. Problems such as hypertonia, dystonia, hypotonia, dyspraxia are unfamiliar to those who approach the issue from a purely orthopedic point of view.
Therefore, it is essential that the team of specialists share diagnosis, objectives, therapeutic indications, and, of course, results.
The professor emphasized the need to intervene with Preventive Functional Surgery, which allows biological correction of lever arms and muscle actions through various types of minimally invasive surgeries such as:
Lever arm surgeries:
- Slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE)
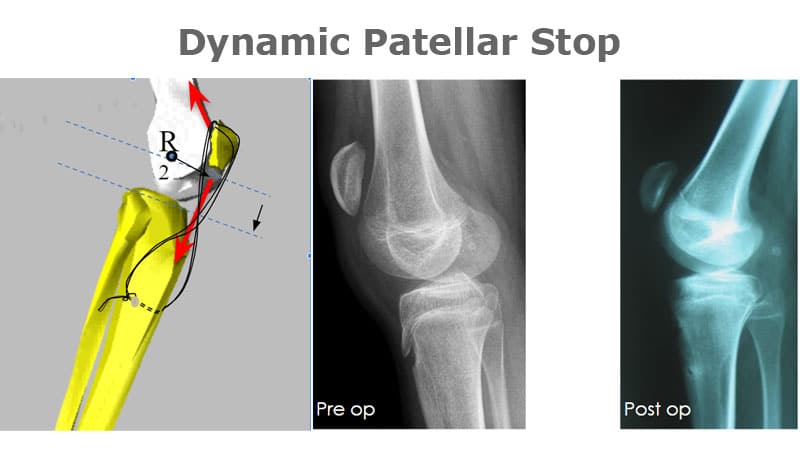
- Dynamic Patellar stop
- Valgus/Varus osteotomy
- Extensor epiphysis
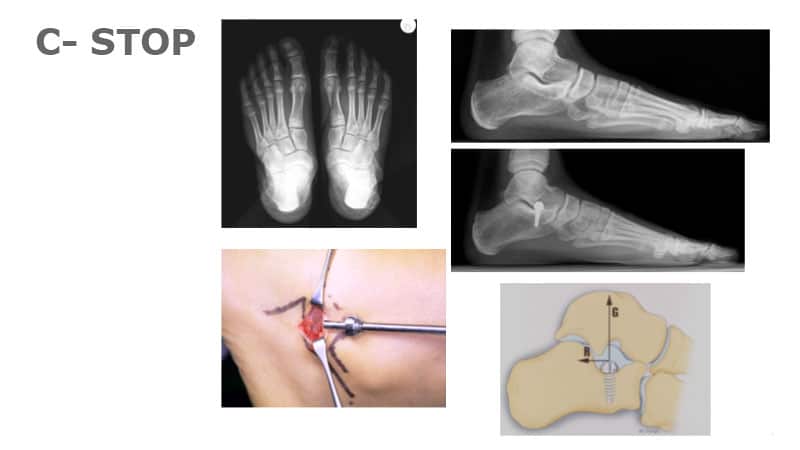
- Foot correction
Surgeries related to Muscular action
- Rectus femoris transfer
- Semitendinosus transfer
- Anterior/posterior tibial transfer
- Sec White lengthening
- Percutaneous Achilles tenotomy
At first, Prof. Portinaro focused more technically on some of the aforementioned types of surgeries. He gave some examples of surgical operations he carried out in collaboration with Fondazione Ariel (a non-profit organization he is scientific director of).
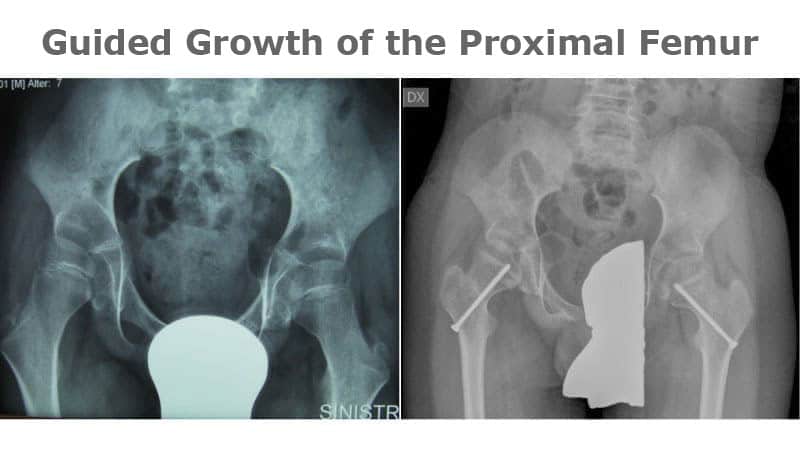
Then the professor concluded his speech by underlining the undisputed advantages that he experienced over the years thanks to this approach. The outcome of his method has also been the subject of several scientific publications at the international level (Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics: Guided Growth of the Proximal Femur for the Management of Hip Dysplasia in Children With Cerebral Palsy Muscle, Ligaments and Tendons Journal: Tendon structure and extracellular matrix components are affected by spasticity in cerebral palsy patients)
Prof. Portinaro also provided a quick overview of the possibilities of late orthopedic surgery. Such surgeries may be performed, for example, to correct structural defects at an age between 12 and 14 years.
He brought some concrete examples of clinical cases he followed by himself, such as
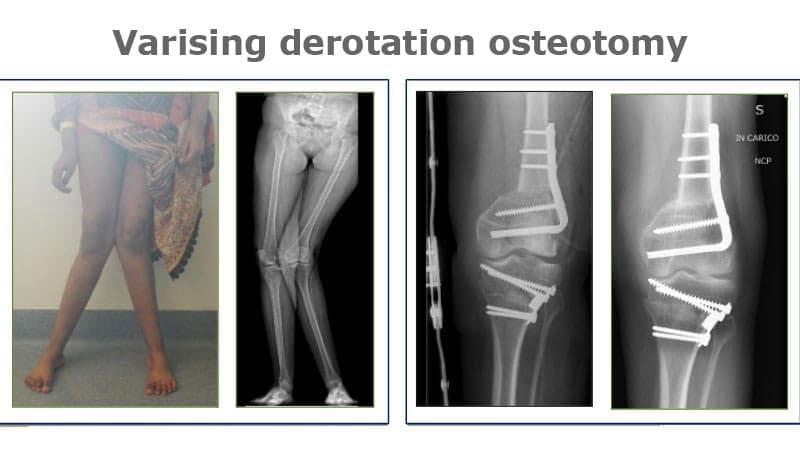
- DVO: centring osteotomy with variation and derotation
- PAO: periacetabular osteotomy
- Head resection
- Panrelease
- Valgus osteotomy
- Extension osteotomy
- Tibial osteotomies
- Foot osteotomies
But the aim of the multidisciplinary team should be to avoid late surgery, anticipating it with an early and multi-level approach that allows much less invasive operations and offers countless advantages, such as:
- Low complexity
- Minor complications
- Immediate physiotherapy
- Progressive and not drastic correction
- Correction of biomechanics
- Optimization of residual muscular potential
The professor’s Lectio took place during a congress that had set itself the objective of offering physiatrists a guiding thread that could help them orient themselves in their training choices and the critical evaluation of emerging technological proposals.
In addition to his lecture, there were others with explicit methodological content on experimental design, psychometric statistics, bibliometrics, and ‘evidence-based medicine’.